Butyric acid is actually not far from us at all. It is a metabolite produced by certain gut bacteria through the metabolism of dietary fiber.
Butyric acid
As a classic short-chain fatty acid, butyric acid is well-known for its ability to repair the intestinal barrier, a benefit widely recognized by the public. However, today the focus is on the mechanisms by which butyric acid aids in weight loss, which primarily encompass two aspects.
One aspect involves inhibiting inflammation, while the other involves boosting metabolism.

Inhibiting inflammation
Butyric acid serves as an inhibitor of HDAC (histone deacetylase), a well-studied target in cancer research. HDAC reduces the acetylation level of histones in the body through its deacetylation activity.
The level of acetylation directly affects chromatin structure and the normal expression of numerous genes. When acetylation levels are reduced, it can trigger inflammatory reactions, neurodegenerative diseases, and tumors. Therefore, many anticancer and antiviral drugs inhibit HDAC, combined with other drugs such as PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4, to achieve breakthroughs in the treatment of solid tumors.
Butyric acid's ability to inhibit HDAC not only ensures normal levels of histone acetylation but also induces apoptosis in various inflammatory cells and cancer cells.
Boosting metabolism
Butyric acid can bind to and activate different G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), increasing the levels of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and peptide YY (PYY).
If you're unfamiliar with GLP-1, that's okay. Just knowing about the weight loss star medications semaglutide and tirzepatide is enough. Because the key to the rapid weight loss achieved by these star medications is GLP-1. Taking semaglutide as an example, it enhances insulin secretion and inhibits glucagon secretion by activating GLP-1 receptors, reducing food intake, thereby achieving the goals of lowering blood sugar and losing weight.
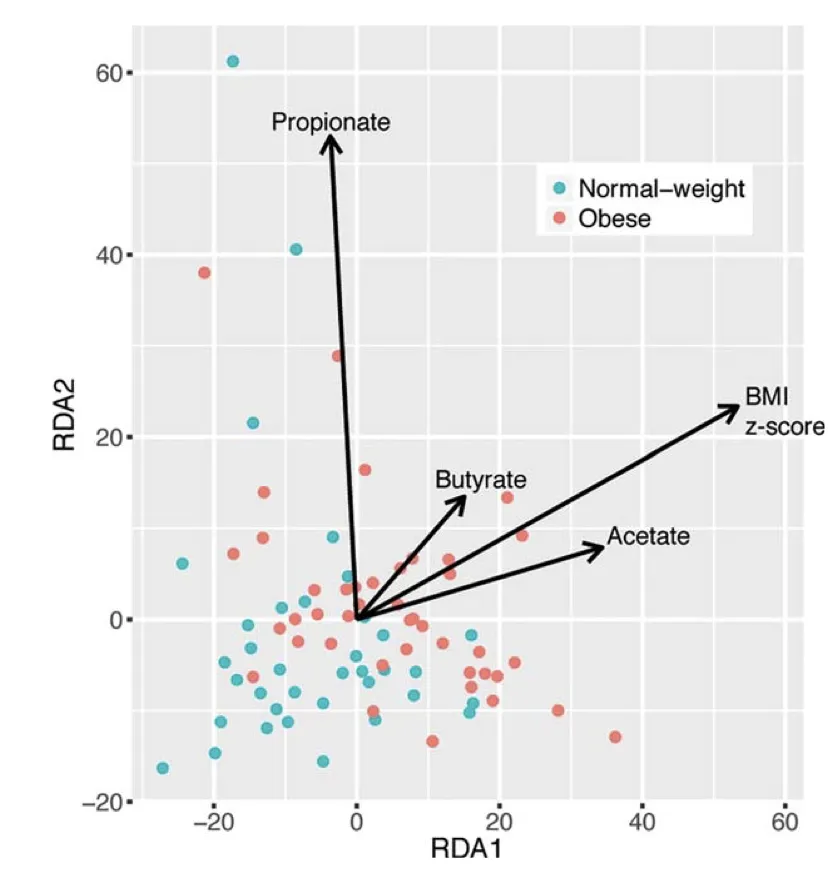
When the level of butyrate salts decreases in your body, it can impact metabolism, a phenomenon particularly evident in obese individuals. For instance, scientists have found that in overweight or obese people or animals, the levels of short-chain fatty acids, especially butyric acid, are significantly lower compared to healthy individuals or animals.
From this, we can further conclude that individuals with low levels of butyric acid also exhibit an imbalance in the structure of their gut microbiota, with the abundance of bacterial strains capable of producing butyric acid being much lower than normal levels.
There are indeed many other factors associated with low levels of butyric acid. These include the loss of GLP-1 response, insulin resistance, elevated levels of inflammatory factors, impaired glucose metabolism, and damage to liver cell mitochondria, among others. These are all key signals contributing to obesity.
Additional research has shown that butyric acid significantly reduces weight
There is actually a considerable amount of research on the intervention of butyrate salts in weight management, both in animal and human trials. However, the direction of these studies is quite similar, with most focusing on oral supplementation of butyrate salts and assessing their intervention on various metabolic functions. This includes examining whether they can significantly reduce weight gain, decrease body fat, and lower insulin resistance.
Supplementing with butyrate salts without the need to change food intake (such as with a high-fat diet) can still significantly reduce high blood sugar issues, increase insulin secretion, and greatly reduce body fat.
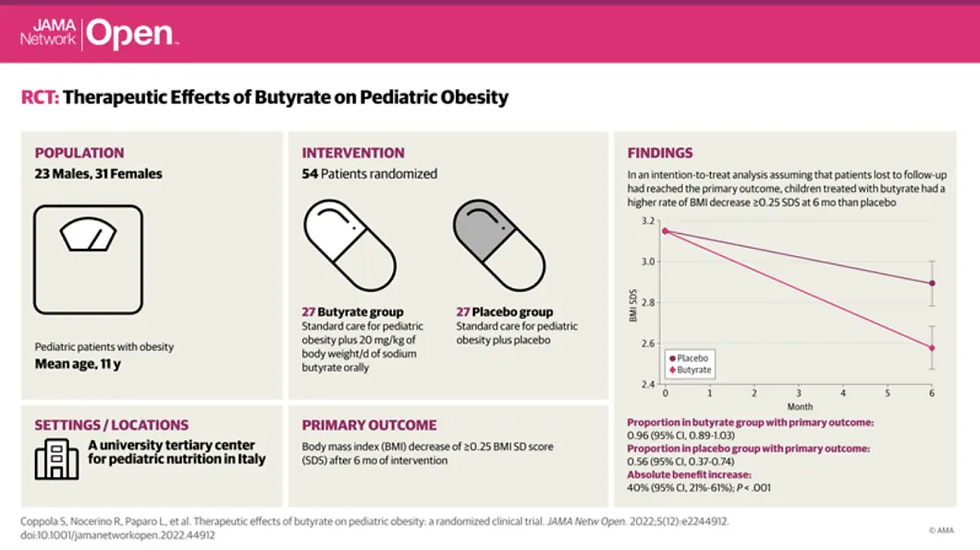
A more authoritative clinical trial from 2022, published in the JAMA journal, was a randomized, controlled, quadruple-blind trial. The study results indicated that, without any other interventions such as medication, solely taking butyrate salts for 6 months significantly reduced the BMI index of obese children.
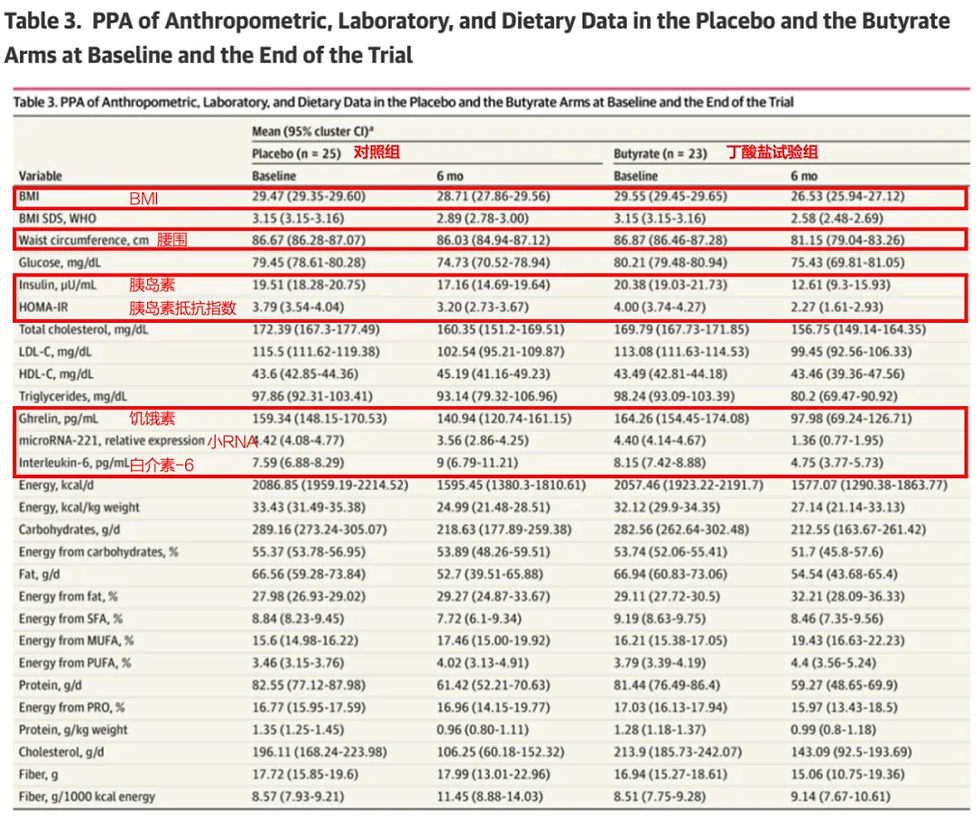
Of course, besides BMI, other weight loss indicators might pleasantly surprise you. By the end of the 6-month trial, obese children who took butyrate salts showed significantly reduced waist circumference (by more than 5cm), insulin levels, insulin resistance levels, ghrelin and IL-6 levels, as well as a more significant decrease in the expression level of microRNA221 compared to the control group.
A clinical controlled study involving 60 type 2 diabetes patients demonstrated that butyrate salts can increase GLP-1 concentration. When combined with inulin intake, they can significantly reduce the waist circumference of diabetes patients and lower fasting blood sugar levels, yielding remarkable results with minimal effort.
Even for healthy individuals, oral supplementation of butyrate salts can significantly improve insulin sensitivity, reduce insulin sensitivity index, and lower the probability of developing diabetes.
Another key to reducing weight, besides improving insulin sensitivity and stabilizing blood sugar metabolism, is the impact on fat metabolism.
Butyric acid "dissolves fat" reducing waist circumference
One of the currently most recognized targets for weight loss is to activate brown adipose tissue thermogenesis while inducing the conversion of white adipose tissue into brown adipose tissue. Interestingly, butyrate salts happen to possess both of these effects simultaneously. They not only promote the conversion of white adipose tissue (WAT) but also significantly activate the activity of brown adipose tissue.
In a 2017 study, the results showed that butyrate not only controls weight by reducing food cravings but also, more importantly, promotes the expression of uncoupling protein 1 (UCP-1) in brown adipose cells, thereby activating the thermogenic function of brown adipose tissue.
If the UCP-1 gene is specifically expressed in brown adipose cells, another crucial gene, LSD1 (lysine-specific demethylase 1), which is an important regulator of thermogenesis, is expressed in both white and brown adipose cells. Experimental results indicate that butyrate salts can increase the browning of white adipose tissue and increase heat production by activating the expression of LSD1.
Because the volume of white adipose tissue is larger than that of brown adipose tissue, during this conversion process, it's as if the fat is "dissolved," resulting in a reduction in volume, thus naturally reducing waist circumference.
Additionally, it's important to emphasize that the activation of brown adipose tissue has been determined to have a significant impact on insulin sensitivity, thus allowing for the reduction of insulin resistance from different perspectives.
During the "fat-dissolving" process, in addition to activating and increasing the expression of specific genes, butyrate also decreases certain small RNA fragments, thereby inhibiting the formation of new fat.
For example, microRNA-221 is one of the most thoroughly studied microRNAs in this context. For instance, in obese individuals with higher levels of insulin resistance and inflammation, the levels of microRNA-221 are significantly higher compared to healthy individuals.
Butyrate salts cleverly seize this opportunity by rapidly reducing the expression of microRNA-221, producing a "lipid-depletion" effect similar to that of surgical weight loss interventions, providing a fat intervention for obese patients.
Of course, besides aiding weight loss, butyrate also has a friendlier effect for overweight individuals, which is reducing the brain damage caused by obesity. Many people often feel that their memory declines significantly after gaining weight, and there is scientific basis for this perception.
Aiding in improving the cognitive abilities of overweight individuals
In our brains, there is a substance called brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy cognitive levels. Once a person or animal becomes obese, the levels of "serum neuroinflammatory toxin" 【 Quinolinic acid 】increase.
This substance, as its name suggests, is not auspicious, and naturally doesn't bring about anything good. Elevated levels of quinolinic acid significantly reduce the levels of BDNF. When BDNF is reduced, it can lead to issues such as synaptic deficits in the brain and a decline in cognitive abilities.
Because butyric acid can precisely reverse this damage. It can inhibit the expression of HDAC2 at the protein level (just remember that HDAC2 has a negative impact on your learning and memory), thereby inhibiting the reduction of BDNF caused by high levels of quinolinic acid and restoring synaptic damage and cognitive abilities. A simple diagram can explain the mechanism here.









コメント